
A Look at the Different Densities of 3D Printing Materials
There’s so much to learn about 3D printing materials. Come and find out what to look for when examining the different densities of 3D printing filaments.
844-810-1385
Temperature—a seemingly innocuous variable in 3D printing—is perhaps the single greatest factor affecting your 3D prints. Like humans, when things are too cold, we don’t perform well. Too hot, and we don’t perform well. We whine; filament just fails.
Before your filament enters the hot end, it’s just a simple spool of glossy plastic. Yet, when the heat rises, a metamorphosis begins, turning a solid into—glass?
Yes, heating a plastic filament is not really melting it (it doesn’t change state) but getting it well above its glass point, where it behaves like liquid glass—thick or thin and able to be pushed around. How we do this is what is really important.
One of the first effects of temperature on 3D printer filament is print precision. A misshapen print may lead us to call the issue a “printer glitch,” but more often than not, our temperature control is the culprit.
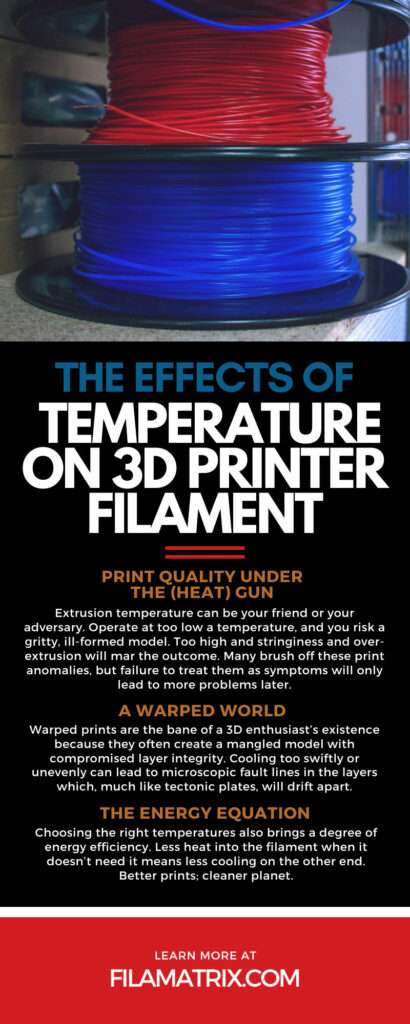
Extrusion temperature can be your friend or your adversary. Operate at too low a temperature, and you risk a gritty, ill-formed model. Too high and stringiness and over-extrusion will mar the outcome. Many brush off these print anomalies, but failure to treat them as symptoms will only lead to more problems later.
Warped prints are the bane of a 3D enthusiast’s existence because they often create a mangled model with compromised layer integrity. Cooling too swiftly or unevenly can lead to microscopic fault lines in the layers which, much like tectonic plates, will drift apart.
The solution might seem straightforward—ensure a consistent cooling rate—but the interplay of materials, their transitory phases, and even the object’s shape can make this more art than science. But you can lay a foundation for a good print and build from there. Maintain a consistent print chamber environment and set all your temperatures to somewhere in the range specified by the filament manufacturer. After all, the manufacturer has probably tested in varying conditions and has a lot to lose when your print comes out distorted.
It’s the unglamorous side of 3D printing—energy consumption. Yet, believe it or not, it directly relates to our management of temperature. The cooling fans, the heated build platforms, and the filaments demand their share of the kilowatts.
But choosing the right temperatures also brings a degree of energy efficiency. Less heat into the filament when it doesn’t need it means less cooling on the other end. Better prints; cleaner planet.
Consistency is the bedrock of sustainable manufacturing, and in 3D printing, temperature control prolongs material life. A filament subjected to wild temperature swings in the printing process might not immediately reveal negative effects, but just because you don’t see it…
Thermal Management Proficiency—that sounds important. But it is an often-overlooked blend of technical skills. 3D printing, like many engineering endeavors, requires control of temperature as well as other variables, as it influences our current creations and future durability and usability. Both manufacturers and hobbyists should realize the importance of precise temperature control as a fundamental aspect of advanced printing methods.
The 3D print industry also continues to adopt advanced thermal control systems, including more precise thermistors, heaters, and real-time software algorithms. These program advancements will eventually make controlling temperature as natural as selecting filament color, if not just as easy.
Copolyester filaments are leading the way in temperature-sensitive polymers. Their unique composition and durability offer stellar print quality and long-term value. They simplify printing by withstanding a wide temperature range (240° C to 270° C) and produce high-strength, durable prints. This filament is not just resilient; it represents a new era in Nylon filament technology. Combining temperature tolerance and material strength challenges industries to create robust and eco-friendly solutions.
The temperature’s interaction with filaments doesn’t end with the last extrusion. Many post-processing techniques—whether annealing, smoothing, or dyeing—start with heat. Materials science is complex, but the main thing to realize is that these materials require some heat to awaken before transitioning to the final, desired state.
The challenge lies in the practice here, not the theory of knowing how much impact heat has in shaping materials. It is a prominent factor in our post-processing practices, and it is critical to always set the right temperature. Even being off by one degree could create a preventable error.
Temperature is no fleeting guest in the 3D printing party; it’s the unassuming architect, the invisible artist, and the tireless overseer of a process that’s both forward-looking and present today.
We must print at a temperature and with temperature in mind. In short, read your filament manufacturer’s instructions for recommended settings before starting to avoid unwanted deformations. From quality to sustainability, from longevity to the soul of creation, our awareness and mastery of the effects of temperature will sculpt our prints and the future of 3D printing.
To plunge deeper into the world of temperature and 3D printing, engage with the 3D printing community (and us!). Join the conversation, experiment with this versatile material, and redefine the boundaries of what’s achievable by controlling the heat.
Take the temperature leap with Filamatrix’s copolyester filament and give your 3D prints a long and strong future.
Filamatrix
NEVER. FEEL. LIMITED.

There’s so much to learn about 3D printing materials. Come and find out what to look for when examining the different densities of 3D printing filaments.

Those interested in 3D printing have a lot to learn on how to use the system properly. Find out what you need to know about 3D printing and humidity levels.

Filaments print differently and yield varying quality results. What about quality variations within a filament family due to color? Let’s take a deeper look.
Get professional insights, industry news, and our latest deals