
A Look at the Different Densities of 3D Printing Materials
There’s so much to learn about 3D printing materials. Come and find out what to look for when examining the different densities of 3D printing filaments.
844-810-1385
Many industries employ designers who create prototypes for machines, products, and buildings. However, the objects they create need flexibility in order to be functional; using filaments to create these items is the best way to add elasticity. Find out how you and your team can benefit from using nylon 3D filaments and learn about the most common applications for this material.
A nylon filament is a thermoplastic, also known as a synthetic polymer. When thermoplastic comes into contact with a heat source, it softens and eventually melts. Conversely, it hardens when put through a cooling process.
Several 3D printing processes use nylon filaments, including selective laser sintering and injection molding. The material has impressive properties, but it does possess certain drawbacks as well.
Nylon filaments have outstanding characteristics, but before working with the fiber, you need to learn about its properties and the drawbacks that surround manufacturing items with this material.
Nylon is a rigid strand, but it is not as stiff as polylactic acid (PLA) or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Nylon is flexible compared to these two materials, meaning its structure isn’t as finite as parts made using PLA.
The great thing about nylon is that it is resistant to many things, including corrosion and heat. When it goes through the quality control portion of the manufacturing process, it tends to pass more tests than other materials because it resists damage from sudden impacts or being submerged.
Nylon is one of the most preferred filaments in 3D printing, but it has drawbacks. Below are the top three disadvantages of using this material, as well as solutions to the problems.
Printing projects can experience problems, especially if there’s an issue with the print material before it is even processed through the 3D printer. If a filament is moist, it will print with a foggy surface that has bubbles or holes on the exterior. When the surface becomes rough, or bubbles and holes appear, the final product’s abilities and strength decrease.
When printing with nylon, ensure you know the right temperature to use; otherwise, your project will quickly become a disaster. The ideal temperature to print nylon is between 230 and 260 Celsius, and the build plate must be between 40 and 70 Celsius.
Warping is a problem in many projects requiring moisture-sensitive materials; warping can occur when the print filament is exposed to changing temperatures. The best solution to warping is to use a printer with an enclosed chamber that controls the amount of heat used throughout the print.
As mentioned above, moisture can present problems for your print. Nylon is hygroscopic, which is why your fiber may experience moisture buildup. When water absorbs into nylon fibers, it creates faulty final pieces. By storing your filaments in a dry, cool place, you can prevent moisture exposure altogether. However, it’s not the end of the world if some water does accumulate on the material. In this case, all you need to do is dry the filament at the manufacturer’s recommended settings to remove the excess moisture.
3D printing is a fascinating process that can be used in many interesting ways. From applications in tooling to prototyping and creating end-user products for the entertainment and retail industries, there’s no end to how you can use nylon 3D filaments; here are the most common applications for nylon 3D filaments.
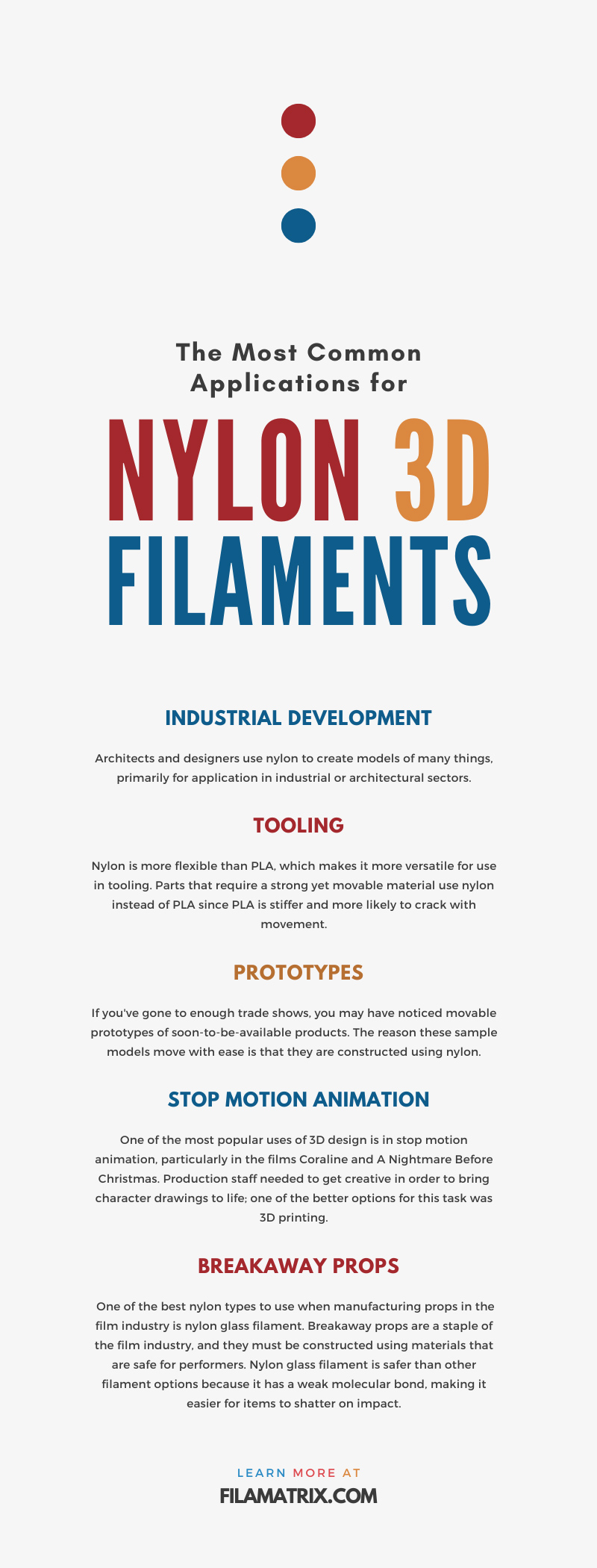
Architects and designers use nylon to create models of many things, primarily for application in industrial or architectural sectors. Although there’s plenty of creative liberty in designing structures, designers have a vast demand for parts that can’t be designed by hand, which is why they use nylon.
Nylon is flexible, making it possible to capture design details with great accuracy. Makers 3D print nylon to create or assemble structures that feature complex designs, leading to more cohesive models.
Industries that utilize metal parts rely on design machines that can quickly create the tooling they need for their devices. As mentioned, nylon is more flexible than PLA, which makes it more versatile for use in tooling. Parts that require a strong yet movable material use nylon instead of PLA since PLA is stiffer and more likely to crack with movement.
If you’ve gone to enough trade shows, you may have noticed movable prototypes of soon-to-be-available products. The reason these sample models move with ease is that they are constructed using nylon. Nylon is a high-quality material that allows manufacturers to refine their designs until they can work out the kinks.
The film industry is no stranger to nylon, as it is often used to create breakaway props. Because of nylon’s profound elasticity, these objects are easier to hold and throw. Entertainers won’t feel a thing when hit with bottles, plates, or blocks that have been printed with nylon.
3D design has come a long way since its invention, and it has played a part in shaping every industry into something entirely new. One of the most popular uses of 3D design is in stop motion animation, particularly in the films Coraline and A Nightmare Before Christmas. Production staff needed to get creative in order to bring character drawings to life; one of the better options for this task was 3D printing.
Throughout production of the stop motion film Coraline, designers made over 6,000 faces to ensure the characters looked authentic and less digitized. These faces were created using various forms of filament, including nylon. Nylon’s flexibility made it easy to morph a face or angle a character’s hand in a way that looked more realistic to audiences.
Nylon filament is available in several forms, each providing unique benefits to various industries. One of the best nylon types to use when manufacturing props in the film industry is nylon glass filament. Breakaway props are a staple of the film industry, and they must be constructed using materials that are safe for performers. Nylon glass filament is safer than other filament options because it has a weak molecular bond, making it easier for items to shatter on impact. The easier these items break, the less harm comes to entertainers who must take a breakaway vase to the head for a scene.
Filamatrix offers businesses many different nylon 3D filaments that they can use to create fantastic end-products. Our assortment of filament choices will ensure you never feel limited by what you can create. Reach out for more information on our products or to learn more about glass nylon filaments.

There’s so much to learn about 3D printing materials. Come and find out what to look for when examining the different densities of 3D printing filaments.

Those interested in 3D printing have a lot to learn on how to use the system properly. Find out what you need to know about 3D printing and humidity levels.

3D printing has many variables that both beginners and experts need to know. Find out what effects temperature has on 3D printer filament.
Get professional insights, industry news, and our latest deals